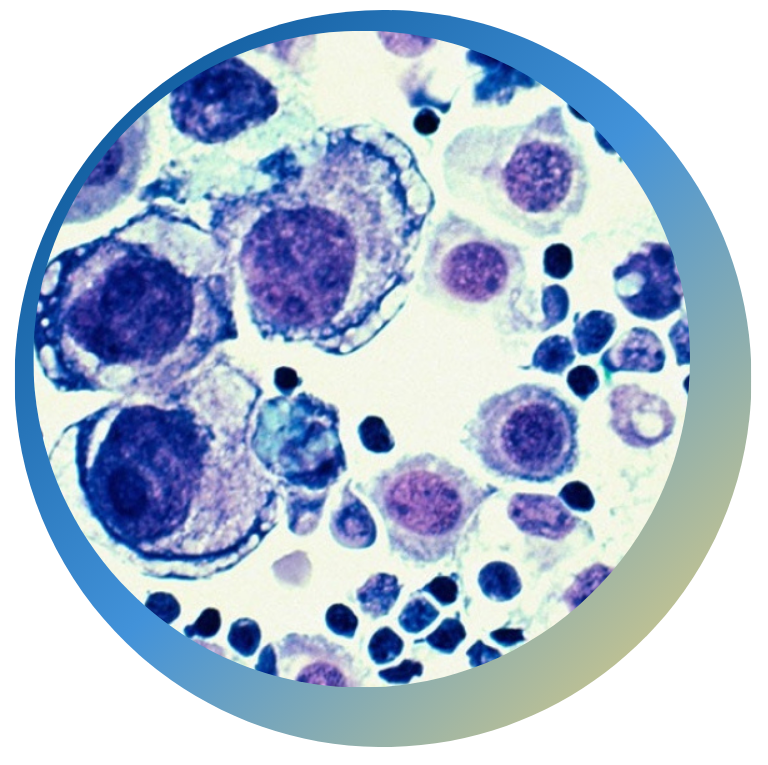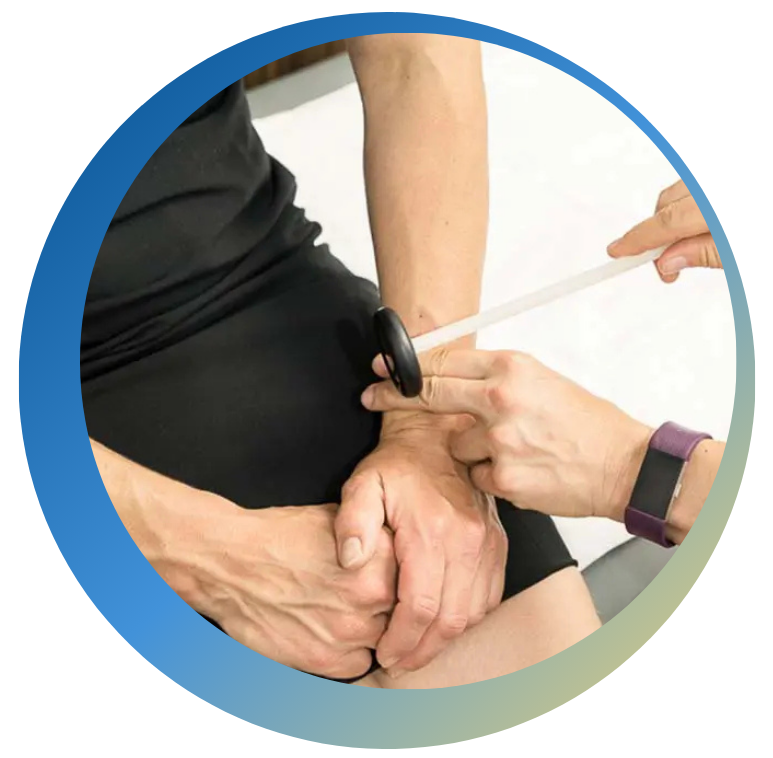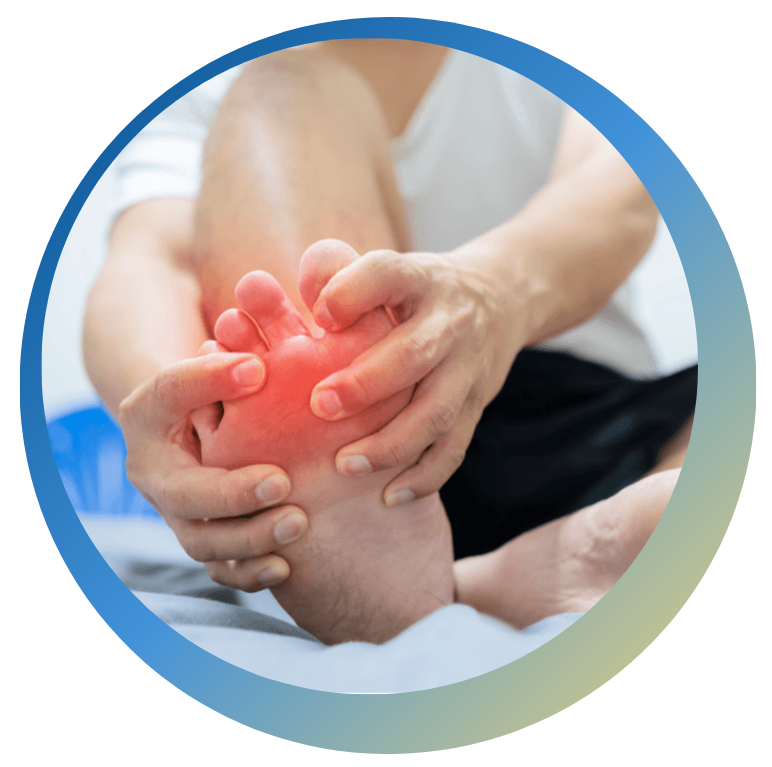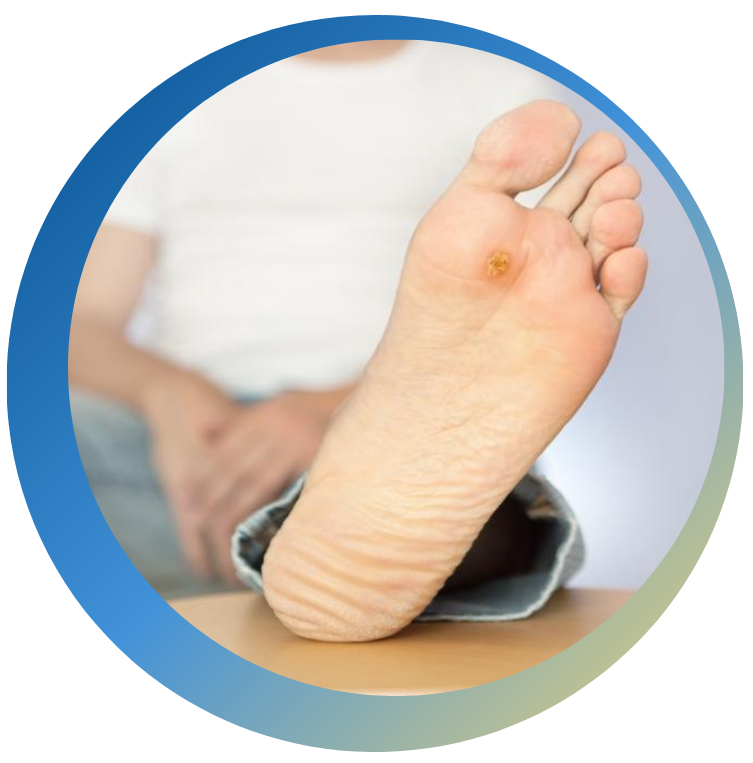
The peripheral nervous system serves an important function, which is to make the person aware that there is possible tissue damage or a dangerous element in their immediate environment. Normal function of the nervous system is such that pain is an indicator of imminent or actual harm to a body part, which results in protective reflexes that will either prevent or minimize the damage. The term for this type of pain is nociceptive pain. It’s generally described as sharp, aching, throbbing type of pain. When pain occurs without any noxious stimuli or threat of imminent harm, this is termed neuropathic pain. It is maladaptive or dysfunctional and does not serve any purpose for the nervous system. Typically, the sensations are described as tingling, shooting, or stinging.

Myelination, or insulation of the nerve fibers, allows them to carry nerve signals at a very rapid rate to the central nervous system. There are typically not associated with pain. Large nerve fibers are responsible for motor function, vibration perception, positional sense and perception of temperature. When the large fibers don’t work well dysfunction is characterized by numbness, tingling, weakness and loss of deep tendon reflexes.
Find out what your doctor isn’t telling you about pain management.